Introduction
Every year, the world comes together to battle Pneumonia on World Pneumonia Day. There has never been a greater pressing need to battle the leading infectious cause of death in both adults and children considering the current dangerous statistics.
In 2019, Pneumonia alone claimed the lives of 2.5 million people, including 672,000 kids. Millions more people are at risk of contracting the disease and dying as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and climate change. The risk of catching Pneumonia is high in the elderly and infants. Children are especially at risk in communities where immunization rates are dropping, malnutrition rates are growing as a result of food shortages, and houses utilize polluting fuels for cooking and heating.
The following blog contains a detailed account of what pneumonia is, what are its symptoms, stages, and causes along with its treatment options.
What is Pneumonia?
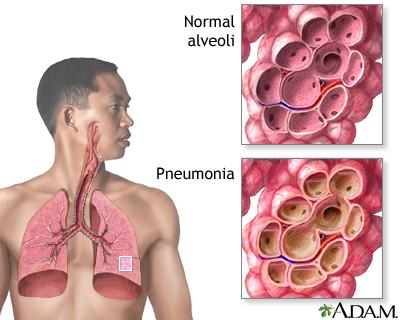
Pneumonia is a respiratory disorder in which the air sacs in one or both lungs catch inflammation. The inflammation can cause fluid or pus to fill the air sacs which results in its swelling. Air sacs have ventilation, diffusion, and perfusion as the primary role, any accumulation in air sacs causes breathing difficulties along with fever, chills, and cough with pus or phlegm.
Pneumonia is usually treatable but can be life-threatening if not treated timely. Infants, young children, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immunity are most vulnerable to pneumonia.
Types of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is classified into four different types based on the way or location it is acquired;
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia is the type of pneumonia that is initially not present in the patients at the time of admission but during their stay at the hospital, they acquire it. Clinically HAP is known as Nosocomial pneumonia. HAP is believed to be more dangerous than other forms of pneumonia as it is coupled with increased antibiotic resistance.
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
Pneumonia that is acquired outside of a hospital is called CAP. This type of pneumonia can manifest itself clinically in various ways. It can cause mild pneumonia with a lingering cough and fever, whereas in serious conditions, it can also cause sepsis with respiratory failure.
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
A person using a ventilator may contract a lung infection known as ventilator-associated pneumonia. By supplying oxygen through a tube put in the patient’s mouth, nose, or through a hole in the front of the neck, a ventilator is a device that assists a patient in breathing. If bacteria enter the patient’s lungs through the tube and divide, an infection could develop leading to VAP.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs as a consequence of the invasion of bacteria into the lungs. Bacteria are capable of entering the respiratory ways via food, drinks, or even saliva. If you have trouble swallowing or are very sleepy from using alcohol, or other sedatives, it’s more likely to happen.
What are the signs and symptoms of Pneumonia?
There are many signs and symptoms which indicate that one has got Pneumonia. These symptoms usually develop in around 24 to 48 hours and in some cases take several days to develop. A patient having pneumonia may experience the following;
- Dry coughing
- Cough with yellow, green, or blood-containing mucus
- Shallow breathing
- Breathlessness
- Increased heartbeat
- Increased body temperature
- Fatigue
- Increased sweat
- Decreased appetite
- Pain in the chest followed by cough
Some people with pneumonia also experience
- Haemoptysis (blood in cough)
- Headache
- Sickness and tiredness
- Muscle and joint pain
- Wheezing
- Confusion and disorientation in elderly
If you are experiencing the symptoms of pneumonia, don’t delay and book an online appointment today using Sehat Kahani’s mobile application. Our experts excel at making a sound diagnosis. You can also book laboratory tests for yourself or your loved ones and avail amazing discounts from our trusted lab partners.
What are the causes of Pneumonia?
When pathogens or germs enter your lungs, it can lead to pneumonia. Inflammation is the response that is caused by the air sacs of the lungs to fight an existing infection. This inflammation leads to the accumulation of pus and fluid in the air sacs which clogs them, causing pneumonia-like symptoms. The main causative agents of pneumonia are bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Bacterial Pneumonia
As the name suggests, a lung infection caused by specific bacteria is called bacterial pneumonia. Streptococcus (pneumococcus) is the most typical type of bacteria that causes bacterial pneumonia. However, other bacteria including Mycoplasma pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, and Legionella pneumophila might also be the culprit. These bacteria can dwell in your throat unharmed if you’re young and generally healthy.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is mainly caused by respiratory viruses. The most common causative agents include influenza (flu) virus, chickenpox virus (varicella-zoster virus), coronavirus, rhinovirus, human metapneumovirus (HMPV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles virus, adenovirus, etc.
Fungal Pneumonia
Pneumocystis jirovecii is a special type of fungi that is the leading cause of fungal pneumonia. Individuals having compromised immunity and chronic health disorders are more vulnerable to fungal pneumonia. Fungal pneumonia can also be acquired by soil rich in harmful fungi and from bird droppings. Two other fungi called Cryptococcus species and Histoplasmosis species are also proven to be major causes of Fungal Pneumonia.
What are the different stages of Pneumonia?
Depending on whatever part of the lungs it affects, pneumonia can be categorized as follows:
Bronchopneumonia
A form of pneumonia called bronchopneumonia results in inflammation of the alveoli. Due to narrowed airways, bronchopneumonia patients may experience breathing difficulties. Their lungs might not receive enough air because of the inflammation. Bronchopneumonia symptoms can range from minor to severe.
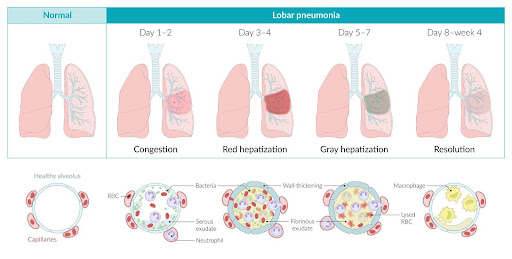
Lobar Pneumonia
Lobar pneumonia is a dangerous infection when pus and other liquids fill the air sacs. One or more lobes (sections) of the lungs are affected by lobar pneumonia. Coughing, increased body temperature, and sputum production are the main symptoms of Lobar pneumonia. The so-called “rusty” sputum has a purulent appearance and may have blood particles in it.
According to the development of the disease, Lobar pneumonia can be further categorized into the following four stages;
- Congestion: In this stage of Lobar Pneumonia, the lungs’ tissue seems dense and weighty. Fluids rich in infectious organisms fill the air sacs.
- Red Hepatization: In the second stage of Lobar Pneumonia immune cells and red blood cells invade the fluids of the lungs giving them a solid red appearance.
- Grey Hepatization: the third stage of Lobar pneumonia is called Grey Hepatization as in this stage the fluid of the lungs turns grey due to the degradation of red blood cells. It is important to note that immune cells persist in the fluid at this stage.
- Resolution: Resolution is the last stage of Lobar Pneumonia as in this stage the infection is starting to be removed by immune cells. The leftover fluid stuck in the lungs can be expelled by coughing.
How is Pneumonia diagnosed?
For the diagnosis of Pneumonia, the medical professional will take your medical history enquiring about the general health conditions and symptoms. If you have the symptoms of pneumonia, then a physical examination is performed using a stethoscope. This will indicate any unusual noises in the lungs. If abnormalities appear in the physical exam, then one or more of the following tests are performed depending on the severity of your symptoms and your risk of complications:
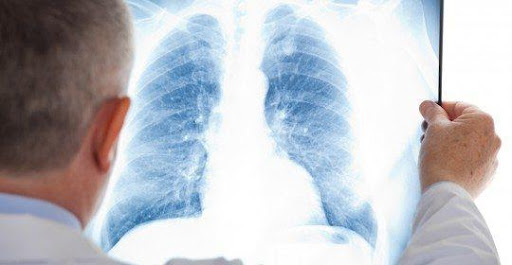
Chest X-ray
Chest X-rays help healthcare professionals in the identification of the location and severity of the inflammation of the lungs.
Blood testing
Blood samples can help to indicate any infections in the body. Additionally, culture can aid in determining what might be the root of your ailment.
Pneumonia culture
A pneumonia culture test is performed on a mucus sample drawn for sputum culture. It is subsequently delivered to a lab for analysis to determine the infection’s origin and causative organism so that appropriate treatment can be given.
Pulse oximetry
The amount of oxygen in your blood is measured with a pulse oximeter. If a sensor is attached to one of your fingertips, it can tell you whether your bloodstream is receiving enough oxygen from your lungs. Fluctuations in normal amounts indicate lung disorders.
CT scan
To diagnose pneumonia that may be harder to notice on a standard x-ray and to see finer features within the lungs, a CT scan of the chest may be performed. A CT scan can assist in a detailed examination of the trachea and bronchi by providing a very detailed image of the airway.
Bronchoscopy
A bronchoscopy examines the lungs’ airways. It is done by gently guiding a flexible tube with a camera on the end down your throat and into your lungs. If your early symptoms are severe or if you are hospitalized and not responding well to antibiotics, your doctor might order this test.
How is Pneumonia prevented?
Following are some useful ways you can prevent pneumonia
Vaccinations
The first and most significant way to prevent pneumonia is to get vaccinated. Today with the advancements in science there are many options available for vaccination. Some major vaccines include Prevnar 13, Pneumovax 23, flu vaccine, and Hib vaccine.
Quit smoking
Try to stop smoking if you do. Smoking increases your risk of respiratory illnesses, including pneumonia.
Maintain good hygiene
Make a habit of washing your hands thoroughly for at least 20 seconds with soap and water. Cover your sneezes and coughs. Throw away used tissues right away.
Improve overall lifestyle
To bolster your immune system, maintain a healthy lifestyle by ensuring sound sleep, a healthy diet, and physical activity.
What are the treatment options for Pneumonia?
The goal of pneumonia treatment is to eliminate the infection and avoid consequences. Community-acquired pneumonia may typically be managed with medicine at home.
The type and severity of pneumonia, your age, and your general health will all affect the specific therapies you receive. The choices of treatment are:
Antibiotics
These drugs are used to treat pneumonia caused by bacteria. Finding the right antibiotic to treat your pneumonia may take some time depending on the sort of bacteria causing it. Your doctor might have to change your antibiotics if your symptoms don’t improve in a day or two.
Cough medication
You can use this medication to reduce your cough so that you can get some rest. It’s a good idea to keep some of your coughs because it helps to loosen and move fluid from your lungs. Use the lowest dose of a cough suppressant that still allows you to sleep if you decide to try one.
Medicine for fever and pain
These medicines are consumed to treat the fever and pain that comes with pneumonia. These include acetaminophen, aspirin, and ibuprofen.
Many cases of pneumonia are treatable with the right diagnosis and care without any negative side effects. Stopping your medications too soon can prevent bacterial infections from completely healing. This suggests that your pneumonia may return. Early medication discontinuation can also increase antibiotic resistance. Infections that are resistant to antibiotics are harder to treat. With at-home care, viral pneumonia frequently gets better in one to three weeks. You could require antivirals in some circumstances. Fungal pneumonia is treated with antifungal medicines. The length of the therapy time could be prolonged.
Summary
Pneumonia is the infection of the lungs caused by fungi, viruses, or bacteria. This causes symptoms like chest pain, a cough that produces mucus or not, a fever, and chills.
Your doctor will do a physical examination and inquire about your medical history to identify pneumonia. They could advise more exams, such as a chest X-ray. Treatment is based on the infection’s underlying etiology. If your symptoms worsen, consult a doctor right away since you might need to stay in the hospital to prevent or treat more serious consequences.





